Table of Contents
ToggleIn a world where kids are glued to screens and their attention spans rival that of a goldfish, teaching them a new language can feel like trying to teach a cat to fetch. But fear not! Child-centric language learning is here to save the day, turning the daunting task of language acquisition into an exciting adventure. Imagine a classroom where laughter echoes, stories come to life, and every word learned feels like a victory dance.
Understanding Child-Centric Language Learning
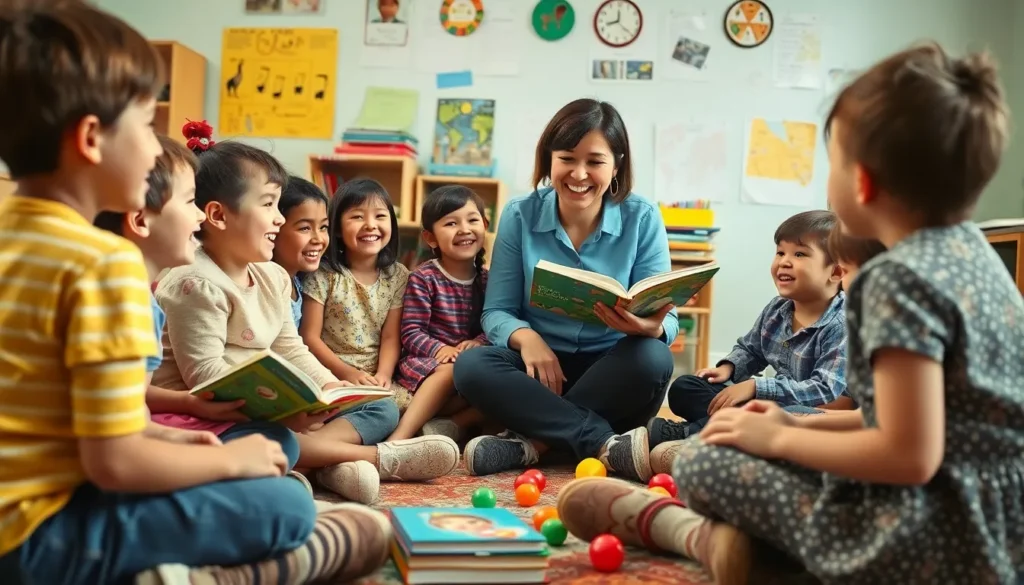
Child-centric language learning focuses on creating an engaging environment for children to learn a new language. This approach emphasizes enjoyment and connection, making the learning process effective and memorable.
Definition and Importance
Child-centric language learning prioritizes children’s needs and interests. This method recognizes that traditional teaching methods often fail to engage young learners. Engaged children demonstrate improved retention and language skills. Studies show that when children enjoy the learning process, they are more likely to embrace new languages and communicate effectively. This approach fosters a love for language and helps develop social skills through interaction and collaboration.
Key Principles
Child-centric language learning incorporates several key principles. It emphasizes interactive activities that cater to children’s natural curiosity. Activities may include storytelling, games, and songs, all designed to enhance learning experiences. Age-appropriate materials ensure that content resonates with learners. Teachers play a vital role by facilitating a supportive environment that encourages exploration and personal expression. Additionally, this approach values the integration of real-life contexts, allowing children to apply their language skills in meaningful situations.
Benefits of Child-Centric Language Learning
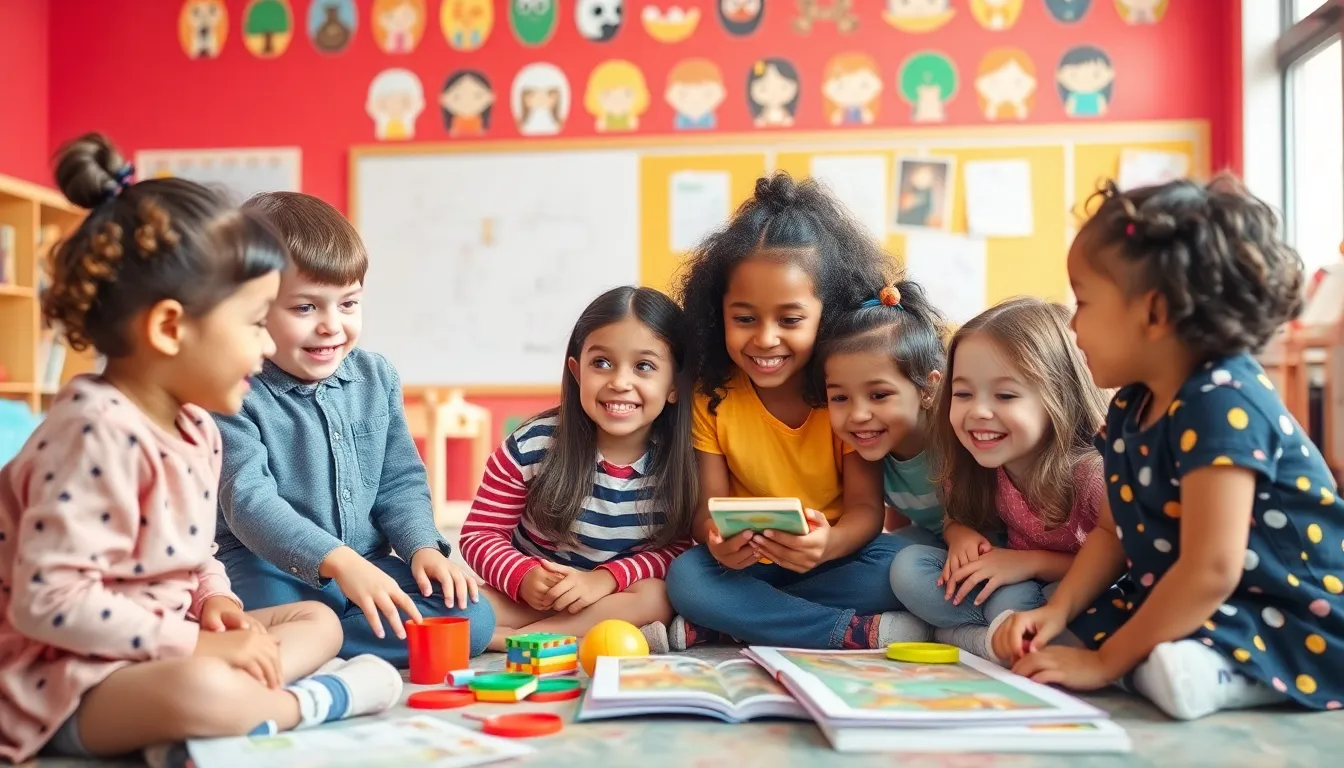

Child-centric language learning provides significant advantages for young learners. This approach prioritizes engagement and enjoyment, leading to better language acquisition outcomes.
Cognitive Development
Cognitive development flourishes through playful language learning experiences. Children who engage with interactive storytelling and educational games often demonstrate improved problem-solving skills. Language learning enhances their memory retention, allowing them to process information more effectively. Studies show that children exposed to rich language experiences develop better critical thinking abilities. Moreover, fostering curiosity leads to deeper understanding, as children explore and connect new vocabulary to their existing knowledge. Structured language activities contribute to developing attention spans and focus, essential tools for academic success.
Social Skills Enhancement
Social skills see marked improvement when children learn languages in engaging environments. Collaborative games and group activities encourage teamwork and communication among peers. Children practicing conversational skills in a supportive setting build confidence in their abilities. Language learning also cultivates empathy, allowing them to understand diverse perspectives. Additionally, sharing stories and experiences fosters stronger relationships and connects them to others. Research indicates that children exposed to varied cultures and languages develop more profound social awareness, which benefits their interactions in multicultural settings. Engaging in language learning thus not only enhances communication but also enriches social cooperation.
Strategies for Effective Implementation
Implementing child-centric language learning involves engaging children through enjoyable methods. Prioritizing their interests fosters a better learning environment.
Interactive Activities
Incorporating interactive activities significantly enhances language acquisition. Storytelling captivates attention, enabling children to absorb vocabulary naturally. Games promote a sense of competition, making learning feel like play rather than work. Songs introduce rhythm and melody, aiding memory retention. Activities that encourage movement engage children physically and mentally. Hands-on experiences solidify language concepts, allowing for practical application. Utilizing tools like visual aids and props adds a dynamic layer, appealing to different learning styles. Each of these interactive elements contributes to a memorable and effective language learning experience.
Inclusive Curriculum Design
Creating an inclusive curriculum design ensures all children feel represented and valued. Incorporating diverse cultures fosters a sense of belonging within the classroom. Age-appropriate materials must reflect children’s backgrounds, interests, and experiences. Lessons that feature relatable contexts increase engagement and understanding. Integrating social-emotional learning enhances the curriculum, teaching skills alongside language development. Collaboration among educators promotes shared resources and innovative ideas. Continuous assessment of the curriculum allows for necessary adjustments, ensuring it meets evolving needs. An inclusive approach supports every child’s journey toward language proficiency, building confidence along the way.
Challenges and Solutions
Child-centric language learning faces several challenges that educators and parents encounter. Understanding these barriers helps in developing effective solutions.
Common Barriers
Short attention spans significantly hinder language acquisition. Children often struggle to remain engaged during traditional lessons, resulting in frustration. Another barrier is the lack of culturally relevant materials, making content less relatable. When resources do not reflect children’s backgrounds, learners may feel disconnected from the language. Additionally, varying proficiency levels within a classroom can complicate group activities. Mixed abilities create challenges in pacing and engagement, limiting opportunities for peer learning.
Effective Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Implementing interactive techniques engages students and fosters enthusiasm. Incorporating storytelling, games, and songs captures children’s interests, promoting active participation. Providing diverse resources ensures representation, making language learning relevant and accessible. Collaborating with peers during group activities enhances social skills and confidence. Adapting lesson plans to address varying proficiency levels allows for tailored support. By utilizing these strategies, educators cultivate an enriching environment that inspires children to embrace language learning.
Child-centric language learning represents a transformative approach that prioritizes children’s enjoyment and engagement. By creating a lively and interactive environment, educators can foster a love for language that transcends traditional methods. This approach not only enhances language acquisition but also nurtures critical thinking and social skills.
As children explore languages through games, storytelling, and collaborative activities, they develop confidence and empathy. The positive impact of this method extends beyond language proficiency, enriching children’s overall cognitive and emotional development. Embracing child-centric strategies allows educators to inspire young learners to connect with diverse cultures and build meaningful relationships, setting the stage for lifelong language appreciation.